Welcome to AltNetPedia. The Cryptocurrency guide. Here you can read about different cryptocurrencies and what they can be used for.
What is a cryptocurrency?

There is no set definition for what is a cryptocurrency and what isn’t a cryptocurrency. Some people would claim that a cryptocurrency is any currency that is based on blockchain technology (or similar). This would make the JPM coin, the coin that JP Morgan is about to launch a cryptocurrency. Others think that a currency needs to have a number of other traits to be considered a cryptocurrency. Example of such traits that would be required for a currency to be considered a cryptocurrency include:
- Anonymity: No one should be able to track who makes which transaction.
- Decentralization: The coin should not be controlled by any one single entity.
- No jurisdiction: The currency should not fall under any single jurisdiction. It should be global.
- No restriction on use: There should be no restriction on how, and for what you can use the currency.
- Floating rate: The currency should have a floating market value against other currencies.
If you think that a cryptocurrency needs to meet these criteria then the JPM coin would not be a cryptocurrency. Something I tend to agree with. The JPM coin seems like a gimmick more than anything else. They simply change the currency of the money JP Morgan keep in the accounts of people who want to keep JPM coins. It can sometimes be hard to say what is, and isn’t a cryptocurrency.
There are no regulations surrounding the term cryptocurrency. Anyone can start a cryptocurrency, and anyone can call any currency a cryptocurrency.
What can you use Cryptocurrencies for?
You can use cryptocurrency to do almost anything you can do with regular currency. There is always someone willing to accept cryptocurrency in exchange for the product or service you want to buy. It is not unusual for sellers to charge a higher price if you want to pay in cryptocurrency than you would have to pay if you paid using another currency. The reason for this is the high volatility of cryptocurrencies. The seller has to make sure that the price he charges in a cryptocurrency is high enough for him to be able to convert it to a regular currency to cover his costs. Prices set in cryptocurrencies can change several times a day.
Investing in cryptocurrencies
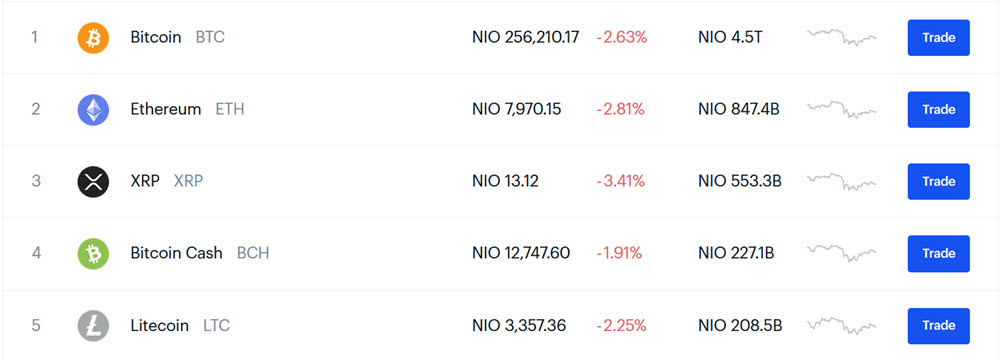
Investing in cryptocurrencies is extremely high risk. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies have gone up and down in value a lot over the last few years. Investing in cryptocurrencies have made some people into billionaires but investing in cryptocurrencies have also cost a lot of people a lot of money. All those who brought Bitcoin at the top have seen their investment lose almost 80% of their value. If you invest in leverage certificates based on cryptocurrencies you can earn or lose even more.
Trading cryptocurrencies can be extremely profitable if you are able to predict the market movements of the currency you trade. If not it is likely to be an expensive experiment that cost you a lot of money. I do not recommend investing in cryptocurrencies if you need the money you invest. Only invest money that you feel comfortable loosing. Read more about investing in/trading cryptocurrencies.
Most people will be better of investing in blue-chip dividend stocks. That is a low-risk long term strategy that is very likely to make you a millionaire. Cryptocurrency is similar to a lottery ticket. You might win big, but you are more likely to lose money.
Why should you use cryptocurrencies?
You do not need to use cryptocurrencies. In fact, there is no reason for most people to use cryptocurrencies. They can be very useful for some things but are nothing that you need in your everyday life. There is no need to use cryptocurrencies for your daily purchases. You can do so if you want to but it is not practical to do. The most widely accepted cryptocurrency is Bitcoin and Bitcoin is unsuitable for most transactions. The value of bitcoin is fluctuating widely making it risky to keep money in Bitcoin, and the transaction fees are very high on small transactions. I really love the idea of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies but the fact is that Bitcoin has turned into something that is unsuitable for most transactions. It was supposed to be a cheap and easy way to trade online but have turned into a very expensive way to buy and sell things as miners have started to charge fees to register transactions in the bitchain. Bitcoin is now only suitable for large transactions where the relative size of the fee is lower.
The only reason to use cryptocurrencies right now is to conceal your identity. If you want to buy something that you do not want to be traceable to you then bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies is a good alternative. It is well known that cryptocurrencies can be used for illegal items such as drugs and weapons. But there are also many legal transactions that you might not want to be traceable to you and where you are willing to pay a premium to stay anonymous. This might include paying for a membership on a porn website or depositing money in an online casino. Two activities that you might not want your partner or anyone else to be able to tell that you engage in. Use cryptocurrency if you want to keep something secret if not, use cash or a regular credit card.
Is Cryptocurrency Real or a Scam?
Cryptocurrency has sparked both excitement and skepticism, with some calling it the future of money and others labeling it a scam. The truth is that cryptocurrency is a legitimate financial technology, with both real opportunities and real risks. Understanding what’s real and what’s hype can help investors and users make informed decisions.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ether (ETH) are decentralized digital assets built on blockchain technology. Unlike traditional money issued by governments, cryptocurrencies operate on peer-to-peer networks. Cryptocurrency is not a scam by default—it is a real, functional technology used globally. However, not all cryptocurrencies are equal, and the industry is full of scams, bad actors, and risky projects.
Simply asking if cryptocurrency is real or a scam will not give you the full picutre. There are many cryptocurrencies that are definitely real, and used in legitimate ways, but cryptocurrencies – and the hype around cryptocurrency – are also utilized by plenty of scammers. When cryptocurrencies became popular in the 21st century, scammers were quick to adapt their schemes and include cryptocurrency as one of lures. Many of the cryptocurrency scams that we see today are simply reworkings of older fraud types, e.g. ponzi schemes, pump-and-dump penny stock scams, investor rug pulls, and fake companies who attract clients and then run away with the money without honoring their obligations.
Why Cryptocurrency is Real
Cryptocurrency is Used for Everyday Transactions
Cryptocurrency and blockchain technology is currently being used for plenty of everyday transactions, including the buying and selling of goods and services online, and the sending of remittances and other international transactions. Cryptocurrency is not simply something that might be used in the future; it is being used here and how.
Adoption by Major Corporations
Companies like Tesla, PayPal, Visa, and JPMorgan have embraced cryptocurrency in some form, whether through payments, investments, or blockchain integration.
Government Regulation and Recognition
While some governments have banned cryptocurrency, many others, including the U.S. and Canada, regulate and tax it. Law enforcements in many countries have also begun confiscating cryptocurrency during criminal investigations, just as they would national currencies and other valuables. This further solidifies the notion that cryptocurrency is real and can have a market value.
Blockchain Technology is Transformational
Modern cryptocurrencies run on blockchain technology; a technology that is also used for other financial applications, supply chain management, and digital security. Even non-crypto industries are adopting it.
Investments
A lot of major investors, including huge investment funds, have allocated some of their resources into cryptocurrency investments.
Inflation Hedge
Many investors are today using Bitcoin as a hedge against the inflation common in national currencies. Unlike national currencies like the USD and GBP, Bitcoin has a limited supply (21 million BTC).
The United States Crypto Reserve
On March 2, 2025, U.S. President Donald Trump announced the creation of a strategic crypto reserve which will include BTC, ETC, XRP, SOL, and ADA. This was the first time Trump specified his support for a crypto “reserve” versus a “stockpile.”
Cryptocurrency Scams
While a cryptocurrency itself can be legitimate, the industry is largely unregulated, making it a breeding ground for scams. Investors should be cautious of projects that promise unrealistic returns, lack transparency, or rely on hype over substance.
Examples of Common Cryptocurrency Scams:
- Pump-and-Dump Schemes
Fraudsters hype up a certain cryptocurrency, drive the price up, and sell before it crashes, leaving unsuspecting investors with big losses. If we look back into history, we can see how this scam is nothing new – but it used to involve penny stocks (and still do sometimes). - Ponzi Schemes
Scammers promise high returns, and then use new investor money to pay older investors until the scheme collapses. It is not unique to the cryptocurrency world, and the scheme actually got its name after a 1920s scammer named Charles Ponzi who claimed to make money from the arbitrage of international reply coupons for postage stamps.
- Rug Pulls in Crypto Projects
Developers launch a new crypto token, collect millions in investment, then disappear overnight, taking investor funds with them. - Fake Cryptocurrency Wallets and Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Some platforms appear to be legitimate but steal users’ funds once deposited. - Celebrity Endorsement Scams
Pretty much all of the scams mentioned above can be boosted by the use of online advertising and social media promotions where well-known individuals are utilized to convince people to invest their money. Sometimes, the celebrity is in on the scam. Sometimes the celebrity is doing the promotion willingly, without realizing they are promoting a scam. Sometimes, scammers simply steal photos of a celebrity and create false campaigns where a project is allegedly supported by Joe Rogan, Elon Musk, Beyoncé, Taylor Swift, etc.
How to Reduce the Risk of Being Scammed
Here are a few examples of what you can do to reduce the risk of being scammed when investing in cryptocurrency.
- New launches are more risky than well-established cryptocurrencies. Many scammers try to convince you to invest in a new cryptocurrency that is about to be launched, promising you vast riches if you get in early. Of course, you can only invest through them.
If you invest in a well-established cryptocurrency instead, such as Bitcoin, you can buy the cryptocurrency on the open market instead of having to go through some “special contact”.
- Look for transparency Legitimate projects have clear whitepapers, development teams, and roadmaps. Information, articles and discussions about the project should exist somewhere else than on a single (clearly biased) site on the internet where the currency is hyped up.
- If it sounds to good to be true, it probably is Avoid projects with guaranteed returns. No real and legal cryptocurrency investment can promise “risk-free” or “guaranteed” profits. Stay clear of anyone who downplays the risks involved with cryptocurrency investing.
- Realize that even legitimate cryptocurrencies can be exploited for scams Just like national currencies are used by scammers, any cryptocurrency – even the large and well-established ones – can be used for scams.
- Use trusted platforms
Well-established exchanges with a good reputation are safer than unknown platforms. - Be wary of hype-driven tokens
If a project is only popular because of social media influencers, memes, and similar, it’s more likely to be a pump-and-dump scheme. - Learn about scams By learning more about common financial scams, you can become better at spotting warning signals at an early stage.
Will Cryptocurrency Replace National Currency?
Cryptocurrency has evolved from an experimental concept to global financial assets, sparking debates about whether cryptocurrencies will replace traditional money. While Bitcoin and other digital currencies offer decentralization and faster transactions, there are still major obstacles preventing them from fully replacing government-issued money. The future of money may include cryptocurrency as a key player, but a complete replacement of traditional currency is unlikely—at least in the near future. Instead, a hybrid financial system where digital assets and traditional currencies coexist seems more realistic. We could also see a future where nations and currency unions (such as the Eurozone) release their own blockchain-based currencies.
What Makes Cryptocurrency a Strong Alternative to National Currencies?
- Decentralization Unlike traditional currencies controlled by governments and central banks, cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized blockchain networks. This means you can pick a cryptocurrency for which no single authority can manipulate supply or restrict transactions. In countries with unstable economies or strict financial controls, cryptocurrency provides a way for people to store and transfer wealth without relying on banks or governments. Note: Some cryptocurrencies are centralized and controlled. If decentralization is important to you, you need to pick the right cryptocurrencies.
- Faster and Cheaper Transactions Cryptocurrencies on the blockchain allow for borderless transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries like banks. Bitcoin and Ethereum transactions can settle within minutes, whereas traditional banking transactions, especially international ones, can take days and involve high fees. Some newer cryptocurrencies, such as XRP and Solana, offer instant transactions with minimal fees, making them a potential alternative to traditional banking systems.
- Limited Supply and Protection Against Inflation Most government-issued currencies, such as the U.S. dollar, can be printed in unlimited amounts, leading to inflation and reduced purchasing power. Bitcoin, on the other hand, has a fixed supply of 21 million coins, making it more resistant to inflation. Some investors view Bitcoin as “digital gold”—a store of value that holds purchasing power over time.
What’s Holding Cryptocurrency Back From Replacing Regular Money?
- Government Control and Regulation
Governments want to control their own currencies to manage monetary policy, taxation, and economic stability. If decentralized cryptocurrencies replaced government money, governments would lose this control, and most of them are unlikely to allow this to happen.
Instead of replacing traditional currency with decentralized cryptocurrency, some governments are looking into developing their own digital currencies. A Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) is a state-backed digital version of a national currency, and it can be controlled by the national central bank just like normal national currency. China, the European Union, and the United States are already exploring Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) as a way to modernize their financial systems while maintaining control.
- Volatility and Lack of Price Stability
One of the biggest obstacles to using cryptocurrency as everyday money is volatility. The price of Bitcoin, for example, can swing 10% or more in a single day against the USD and EUR. People need a stable currency for everyday transactions, as few people want to buy groceries with Bitcoin on Monday only to realize on Tuesday that the amount spent yesterday is now worth 10% more.
Stablecoins, such as USDT (Tether) and USDC (USD Coin), are designed to maintain a 1:1 value with traditional currencies, making them a more realistic alternative for daily transactions. Exactly how these pegs work have been criticized, as several companies have failed to maintain the
transparency and verifiability of its claimed reserves.
- Limited Adoption for Everyday Payments
While some businesses accept cryptocurrency, the majority of global commerce still operates on traditional financial systems. Credit cards, digital payment platforms, and cash are far more widely accepted than cryptocurrency. Until cryptocurrencies gain mainstream adoption, their use as a primary currency will be limited.
The More Likely Future: A Hybrid System
Rather than replacing traditional currency outright, cryptocurrency will likely become a parallel financial system. Governments and businesses will integrate blockchain technology into traditional banking, and some people will choose to store wealth and transact in cryptocurrency, while others will continue using traditional money.
How Cryptocurrency and Traditional Money Can Coexist:
- Governments can issue digital currencies (CBDCs) while allowing private cryptocurrencies to operate alongside them.
- Stablecoins can bridge the gap between cryptocurrency and traditional money, providing stability while keeping the benefits of blockchain technology.
- Businesses and consumers can elect to use cryptocurrencies for specific purposes, such as cross-border payments, investment, or financial privacy, while still relying on fiat currency for everyday expenses.
Is Cryptocurrency an Investment or Speculation?
Cryptocurrency has gained massive popularity as a new financial asset, but the debate continues: is it a legitimate investment or just high-risk speculation? Which answer you will get from the experts depends on several factors, including which cryptocurrency that is being used, how it’s used, and the respondents personal view on cryptocurrency, fiat currency, and other investments. While established cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ether (ETH) are increasingly seen as long-term investments, much of the cryptocurrency market is still fueled by hype and high volatility, making it more suitable for speculation than long-term wealth accumulation. Bitcoin, Ether and a few other cryptocurrencies enjoy institutional adoption and actual use cases, while plenty of other cryptocoins are highly speculative.
The Case for Investing in Cryptocurrency
- Store of Value and Hedge Against Inflation
Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, is often referred to as “digital gold” because of its limited supply (21 million coins) and resistance to inflation. Similar to gold, Bitcoin does not generate income or dividends, but many investors hold it as a long-term hedge against economic instability and currency devaluation.
- Institutional Adoption and Growing Legitimacy
As more companies and financial institutions adopt at least some cryptocurrencies, the argument for cryptocurrency as an investment becomes stronger. Large corporations, such as Tesla and MicroStrategy, have added Bitcoin to their balance sheets, while investment firms like BlackRock and Fidelity offer crypto-related financial products.
- Blockchain Utility and Smart Contracts
The Ethereum network has proven its value through smart contracts, which power decentralized finance (DeFi), NFTs, and blockchain-based applications. Unlike more speculative coins, Ether is the native coin of the Ethereum network, which makes owning Ether more like an investment in future technology than pure speculation.
The Case for Using Cryptocurrency Only For Speculation
- An Exceedingly High Sensitivity to Hype
The cryptocurrency market is notorious for wild price swings, often seeing double-digit gains or losses within days. The price of traditional investments like stocks, commodities, or real estate are – at least to some degree – influenced by economic fundamentals. With cryptocurrencies, we tend to see a much large impact of social media hype, speculation, and market sentiment. Many cryptocurrencies still largely lack real-world use cases and exist purely for speculative trading. Coins like Dogecoin (DOGE) and Shiba Inu (SHIB) were created as jokes but skyrocketed in value due to hype, only to go through various crashes when the excitement faded. Investing in such assets is more like gambling than long-term investing.
Of course, it is not black or white. Penny stocks can swing widely in price during a trading day, the prices of agricultural commodities can drop or rise based on impulsive market sentiments rather than hard harvest data, the price of crude oil can react unpredictably to news events, and so on. Short-term speculation occur on all markets and the traditional markets are certainly not immune to sharp boom and busts brought on by hype.
- Lack of Regulation
Unlike traditional investments regulated by governments and exchanges, cryptocurrency still operates in a largely unregulated space. This creates fertile ground for pump-and-dump schemes, rug pulls, and fraudulent projects, making it difficult to distinguish solid investments from pure speculation.
- Lack of History
A stock investor that wish to stay clear of pump-and-dump schemes can simply avoid penny stocks and only invest in blue-chip stock companies that can show decades of solid book keeping and sound finances. With blockchain cryptocurrencies, this alternative is not possible, as the first blockchain cryptocurrency – Bitcoin – was not launched until 2009.
Examples of Common Cryptocurrencies and Their Uses
Cryptocurrency has expanded far beyond Bitcoin (BTC), with thousands of digital assets serving different purposes. Some cryptocurrencies only act as stores of value, while others power blockchain networks, smart contracts, or decentralized finance (DeFi). Understanding the most common cryptocurrencies can help investors and traders navigate the space more effectively.
Bitcoin (BTC) – The Original Blockchain Cryptocurrency
Bitcoin is the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, created in 2008 by an anonymous person (or group) known as Satoshi Nakamoto. Launched in January 2009, Bitcoin is a decentralized, peer-to-peer currency that doesn’t rely on banks or governments.
Key Features
- Limited Supply. Only 21 million BTC will ever exist, making it resilient to inflation once all the 21 million BTC have been created.
- Store of Value. Many investors treat Bitcoin as “digital gold”, holding it as a hedge against inflation.
- Old and well-established. It was the first of the blockchain cryptocurrencies, it is still the most well-known, and it has the largest market capitalization.
- Bitcoin remains the most dominant and widely accepted cryptocurrency worldwide.
The starting block of the Bitcoin chain (the genesis block) was mined on January 3, 2009. Nine days later, Hal Finney received the first bitcoin transaction – 10 bitcoins send by the mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto. The first known commercial transaction using bitcoins took place in May that year, when the programmer Laszlo Hanyecz paid 10,000 BTC for two Papa John´s pizzas.
In 2010, Satoshi Nakamoto handed the network alert key and control of the code repository to Gavin Andresen, before disappearing. In 2012, the Bitcoin Foundation was established, with Andresen as a lead developer.
Ether (ETH) – The Native Coin of the Smart Contract Platform Ethereum
As the native coin of the network Ethereum, Ether (ETC) is now the second-largest cryptocurrency by market cap and serves as a foundation for smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) on the Ethereum network. Unlike Bitcoin, which mainly functions as digital money, Ether is necessary to use the Ethereum network for programmable transactions, e.g. for DeFi, NFTs, and more.
Key Features
- Ether is the native coin of the Etherum network, where self-executing contracts power decentralized applications. Many different cryptocurrencies can run on the Ethereum network, but Ether is its native coin.
- During the Ethereum 2.0 Upgrade, Ethereum transition from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS), making it faster and more energy-efficient.
- Ethereum is a leader when it comes to non-fungible tokens (NFT:s) and DeFi.
- An investment in Ether is often viewed as a bet on the future success of mart contracts and DeFi, rather than just ownership of digital currency.
Ethereum was conceived by the programmer Vitalik Buterin in 2013, and developed by him and a group of other blockchain pioneers. The network went live on July 30, 2015. By January 2018, Ether had grown to be the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, second only to Bitcoin. In March 2021, Visa Inc. announced that they had begun settling stablecoin transactions using Ethereum.
BNB – A Utility Token for Binance
BNB was created as a discount token for Binance, the world’s largest crypto exchange. Over time, it has evolved into a multi-purpose cryptocurrency and is used for transaction fees, DeFi applications, and payments.
Key Features
- BNB powers the Binance Smart Chain (BSC), a competitor to Ethereum for smart contracts and DeFi apps.
- By using BNB, you get lower trading fees on Binance. Holding BNB gives users discounts on the Binance exchange.
- Binance regularly burns BNB tokens, reducing supply to maintain value.
- BNB’s value is closely tied to the growth and success of Binance and its blockchain ecosystem.
The cryptocurrency exchange Binance is operated by Binance Holdings Ltd. Binance was initially based in China, before moving to Japan as the Chinese government cracked down on cryptocurrency companies. Binance then left Japan for Malta, and is today without any official headquarters. The Binance Coin (today named BNB) was launched in 2017, and by 2021 it had grown to be the cryptocurrency with the third-largest market capitalization. The coin was originally on the Ethereum network, before moving to the BNB Chain (then named the Binance Smart Chain) in 2020.
XRP – Developed For Fast Cross-Border Transactions
XRP, developed by Ripple Labs, is designed for fast and low-cost international payments. Unlike Bitcoin and Ethereum, which rely on mining, XRP transactions are validated by a unique consensus algorithm that makes them much faster. Despite legal challenges, XRP remains a popular choice for global payments.
Key Features
- Transactions are settle in seconds. This blockchain can process 1,500 transactions per second, compared to Bitcoin’s 7 transactions per second.
- XRP is used by several notable financial institutions, including banks and payment providers that utilize XRP for cross-border remittances.
- Ripple Labs has faced a lawsuit from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) over whether XRP is a security or not.
The XRP Ledger, also known the as Ripple Protocol, was launched by Ripple Labs in 2012. The ledger supports tokens, cryptocurrency and other units of value, such as mobile minutes and frequent flyer miles. As mentioned above, the ledger operates on a consensus protocol that differs from both proof-of-work and proof-of-stake mechanisms. Within this ledger, transactions are validated by a network of independent validators who will reach consensus every 3-5 seconds. The trusted list of validators is called the Unique Node List (UNL). While this solution makes transactions very fast, it also means less decentralization.
Cardano (ADA) – A Scalable Blockchain Platform
ADA is the native coin for Cardano, a blockchain platform designed for secure and scalable smart contracts. It aims to improve upon Ethereum by offering a more energy-efficient and academically peer-reviewed system.
Key Features
- The network Cardano, where ADA is the native coin, use Proof-of-Stake (PoS) istead of Proof-of-Work (PoW). This is more environmentally friendly than Bitcoin´s proof-of-work system.
- Cardano has an academic approach and is developed and maintained through scientific research and peer-reviewed technology.
- Just like Ethereum, Cardano supports Smart Contracts.
- Cardano is similar to Ethereum, but with faster processing speeds and lower fees.
- Investing in ADA is commonly seen as a vouch for the future of Cardano.
Cardano is controlled by three entities: The Cardano Foundation, IOHK, and Emurgo. The development and maintenance of Cardano is overseen by the Swiss-based Cardano Foundation, which aims to standardize the Cardano ecosystem. IOHK is the engineering company that builds the Cardano blockchain, and Emurgo is the entity responsible for commercial applications.
Cardano was named after the Italian mathematician Gerolamo Cardano, and ADA is named after the English mathematician Ada Lovelace.
Dogecoin (DOGE) – The Meme Coin That Became a Success
Dogecoin started as a joke cryptocurrency in 2013 but gained mainstream attention thanks to a social media hype. Today, it is accepted by numerous businesses, including Tesla. Unlike Bitcoin, which has a limited supply, Dogecoin has unlimited production, making it sensitive to inflation. Dogecoin remains a highly speculative asset, with value mostly driven by hype.
Key Features
- Originally designed as a fun alternative to Bitcoin.
- Community-Driven. Dogecoin’s value is largely influenced by internet culture and celebrity endorsements.
- Fast and Cheap Transactions. Dogecoin’s target block time is 1 minute, which is much faster than Litecoin’s 2.5 minutes and Bitcoin’s 10 minutes.
- Dogecoin’s blockchain cannot directly interact with smart contracts.
- Dogecoin is often used by internet-based tipping systems where social media users can tip other users that provide useful content.
- When Dogecoin was launched, the intended supply limit was 100 billion DOGE. By mid-2015, the 100 billionth Dogecoin had been mined. Since then, an additional 5 billion DOGE has been put into circulation each year.
Solana (SOL) – The Native Coin of a High-Speed Blockchain
Solana is a high-performance blockchain designed for speed and scalability, and SOL is its native coin. Solana is marketed as an Ethereum competitor, and it can handle thousands of transactions per second, making it a strong choice for DeFi, NFTs, and gaming applications.
Key Features
- Ultra-Fast Transactions. Solana can process 65,000 transactions per second.
- Low fees.
- Popular for NFTs and DeFi. Many blockchain-based games and NFT projects use Solana.
- Energy-Efficient. Solana Uses Proof-of-History (PoH) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
- Solana’s speed and low costs make it attractive, but network outages have raised concerns about its reliability.
Stablecoins – Cryptocurrency Backed by Other Currency
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies backed by a reserve of other currency, usually the U.S. dollar. This makes them much less volatile than regular cryptocurrencies. They are often used for trading, remittances, and storing value without exchange-rate fluctuations. Several different stablecoins have been created, of which two of the most well-known are the Tether (USDT) and the USD Coin (USDC). Tether is the most widely used stablecoin, while the USD Coin is a more regulated and transparent alternative to Tether.
DAI is a stable coin that is not backed by the U.S. dollar nor any other national currency. Instead, it is backed by crypto collateral. DAI (formerly known as SAI) utilizes the Ethereum blockchain, where it uses smart contracts designed to control supply to keep the value of 1 DAI as close to 1 USD as possible. DAI is maintained by MakerDAO, a decentralized autonomous organization composed of the owners of the governance token MKR.
May stablecoins have been criticized for their lack of transparency, and it is difficult for users to know if the reserves are actually as large as promised.
Since they aim to stay pegged, stablecoins are not purchased by investors looking for a rise in value, but they can still be useful for investors looking for a safe-ish haven in times of market turbulence.
